Gynecomastia
(Male Breast Enlargement)
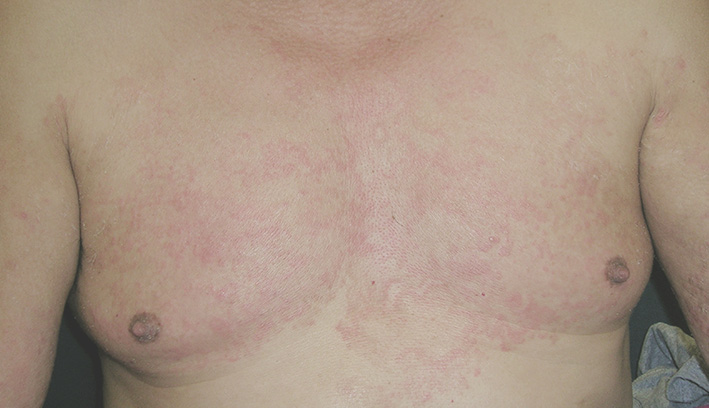
Gynecomastia refers to the condition in which a man's chest appears more prominent or "feminine"
due to an excessive buildup of glandular tissue or fat beneath the areola.
This condition typically affects the lower part of the areola.
Although the risk of breast cancer in men is much lower than in women,
the condition can lead to the development of lumps and cause discomfort or aesthetic concerns.
As natural healing is unlikely, treatment is often necessary. In most cases, surgical removal of the excess tissue is recommended.
Causes of Gynecomastia
(Male Breast Enlargement)

Persistent Gynecomastia After Puberty
Gynecomastia can occur in approximately 30–60% of adolescent males. Around the ages of 10 to 12, when sex hormone production begins, a temporary imbalance between male and female hormones may lead to breast tissue development. In most cases, this condition resolves on its own as hormone levels stabilize during and after puberty. However, if the breast tissue persists into adulthood, it may be diagnosed as gynecomastia
As men age, the production of male hormones decreases, and the relative influence of female hormones increases, which can lead to gynecomastia.
Medication use (such as treatments for peptic ulcers, tranquilizers, medications for benign prostatic hyperplasia, antihypertensives, and hair loss treatments)
Liver diseases (such as cirrhosis), kidney diseases, and hyperthyroidism.
In overweight men, a Westernized diet can lead to fat accumulation in the chest area, giving the appearance of a more feminine breast shape
Gynecomastia Symptoms
A noticeably protruding chest, palpable lumps, and pain.
These symptoms may not only indicate gynecomastia
but can also be seen in conditions such as mastitis or even breast cancer,
so an accurate differential diagnosis is essential.
Gynecomastia Treatment
It is not necessary to begin treatment solely based on the development of breast tissue.
However, if gynecomastia causes discomfort in daily life or becomes a psychological burden, active treatment should be considered.
In cases caused by medication, discontinuing the causative drug is essential.
If there is no improvement after stopping the medication or treating the underlying condition, surgical removal may be required.
What is surgical removal?
Gynecomastia consists of both fat and glandular tissue, so simple liposuction alone is not sufficient for correction.
Glandular tissue excision must be performed together with liposuction.
Since it is a relatively simple procedure with a quick return to daily activities,
those who suspect gynecomastia are encouraged to visit the clinic without hesitation for diagnosis, consultation, and appropriate treatment.
Privée Special