Special Features of Thyroid Care at
Privee Breast & Thyroid Surgery Clinic
Due to the nature of thyroid diseases, early diagnosis and continuous management are crucial.
Privee Breast Surgery Clinic is equipped with a range of advanced diagnostic equipment and
systems to treat thyroid conditions more effectively.
We go beyond simply providing information or taking a one-sided approach to treatment.
Instead, we work closely with each patient to understand their needs and preferences,
and offer patient-centered care focused on identifying and resolving their specific concerns.
Precise and Scientific Examination
Accurate diagnosis by experienced medical professionals through a variety of advanced tests using cutting-edge equipment
Patient-Centered 1:1 Customized Treatment
Tailored solutions to address issues through thorough consultations

Post-Treatment Management System for Recurrence Prevention
Continuous management after treatment to prevent recurrence and improve thyroid function
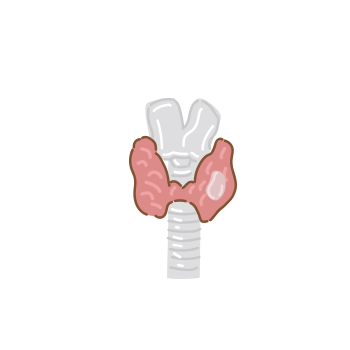
Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid is an organ that produces thyroid hormones essential for basic metabolism.
It is named "thyroid" because it has a shield-like shape.
In a normal person, the thyroid is located just below the "Adam's apple," which is the thyroid cartilage in the center of the neck.
The thyroid is about the size of a thumb and is located on both the left and right sides,
with the central part connected in a band shape, giving it a butterfly-like appearance.
The weight of the left and right thyroid lobes is about 15-20 grams each, and in a normal state, it is not easily palpable.
Function of the Thyroid Gland

Regulates the speed of cell activities
Responsible for hormone secretion

Maintains a stable body temperature

Promotes growth and development of bones and the brain
Our body has hormone-secreting organs called endocrine glands.
The thyroid gland is one of these endocrine organs, and it stores and releases thyroid hormones into the bloodstream when needed.
The primary role of thyroid hormones is to regulate the speed of cellular activity throughout the body.
In other words, when thyroid hormone levels are low, the cells in the body function more slowly, and when levels are high, they become more active.
Thyroid hormones also help regulate body temperature by generating heat, and they play a vital role in the brain and bone development of fetuses and newborns.
Thyroid Exam
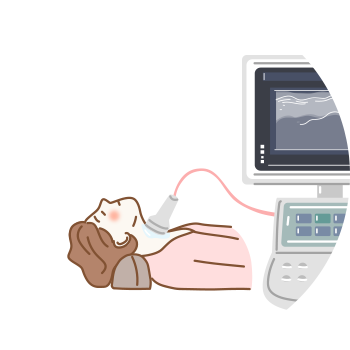
Ultrasound Examination
This is a diagnostic test used to determine the location and size of a thyroid tumor(nodule), among other characteristics.
Ultrasound examination uses sound waves to evaluate the shape, internal structure, and surrounding tissues of the thyroid gland. It is the most effective method for detecting thyroid nodules or cancer. As a non-invasive and radiation-free procedure, it is safe and widely used. Through this exam, doctors can check for the presence, location, and characteristics of any masses, as well as identify other abnormalities in the neck area. If a suspicious nodule is found, a fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) guided by ultrasound is typically performed immediately.
Cell and Tissue Biopsy
This test is used to determine whether a thyroid tumor (nodule) is benign or malignant (cancerous).
A thyroid fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy is performed when a thyroid tumor (nodule) is present, to determine whether the nodule is benign or malignant (cancerous). This test involves collecting a sample of cells or tissue directly from the nodule for examination.
Although it involves extracting tissue from the body, the procedure is simple and safe. After disinfecting the area, a thin needle attached to an empty syringe is inserted into the nodule under ultrasound guidance to collect cells for analysis.
Blood Test
A blood test measures the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood to diagnose thyroid disorders.
If the thyroid produces more hormones than needed by the body, it is called hyperthyroidism; if it produces fewer, it is called hypothyroidism. These thyroid disorders can be initially diagnosed through a blood test. The blood test is an accurate way to assess thyroid function, as it measures the levels of two thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) secreted by the thyroid, as well as the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secreted by the pituitary gland.
Privée Special